Palau Baró de Quadras
Modernism
The Palau Baró de Quadras is a small Modernista palace, built between 1904 and 1906 by architect Puig i Cadafalch. It has been designated a National Historical Monument of Artistic Interest and currently houses the main offices of the Institut Ramon Llull. The building, with a floor surface area of 2000 m2, is located in Barcelona on Avinguda Diagonal, equidistant from La Pedrera and Casa de les Punxes.




Eixample Cerdà
During the mid-19th century Barcelona enjoyed a surge of growth that allowed it to expand and absorb adjoining communities, largely with architect Ildefons Cerdà’s Eixample project as a driving force. It was a period in which some families made their fortunes from the burgeoning industry in the Vallès region, and as a symbol of their wealth, then built grand homes in Barcelona’s downtown Eixample neighborhood. These were lavish and magnificently ornate buildings in which the best Modernista architects and artisans competed to leave their mark on the main streets and boulevards of this new area of the city.
The owners lived on the first floor, known as the pis principal, while the ground floor was used as a commercial space for selling their merchandise, and the apartments above were usually rented.




Puig i Cadafalch: the Architect
Josep Puig i Cadafalch (1867-1956) was, along with Antoni Gaudí and Lluís Domènech i Montaner, one of the most outstanding and renowned Catalan Modernista architects. He built the Palau del Baró de Quadras between 1904 and 1906, during one of the highpoints of his career: he completed Casa Amatller in 1900; Palau Macaya in 1901; Palau Serra (which currently houses the Barcelona Provincial Council) in 1903; Casa de les Punxes in 1905; and the Casaramona factory (currently the CaixaForum) in 1912.
Later on, Puig i Cadafalch designed Plaça d’Espanya and the 1929 Barcelona International Exposition space, as well as numerous other works. On a different front, he was also a dedicated historian, writing about Romanesque architecture in Catalonia, and an archaeologist who spurred the excavation of the Greek ruins in Empúries and the restoration of numerous Romanesque buildings throughout Catalonia.


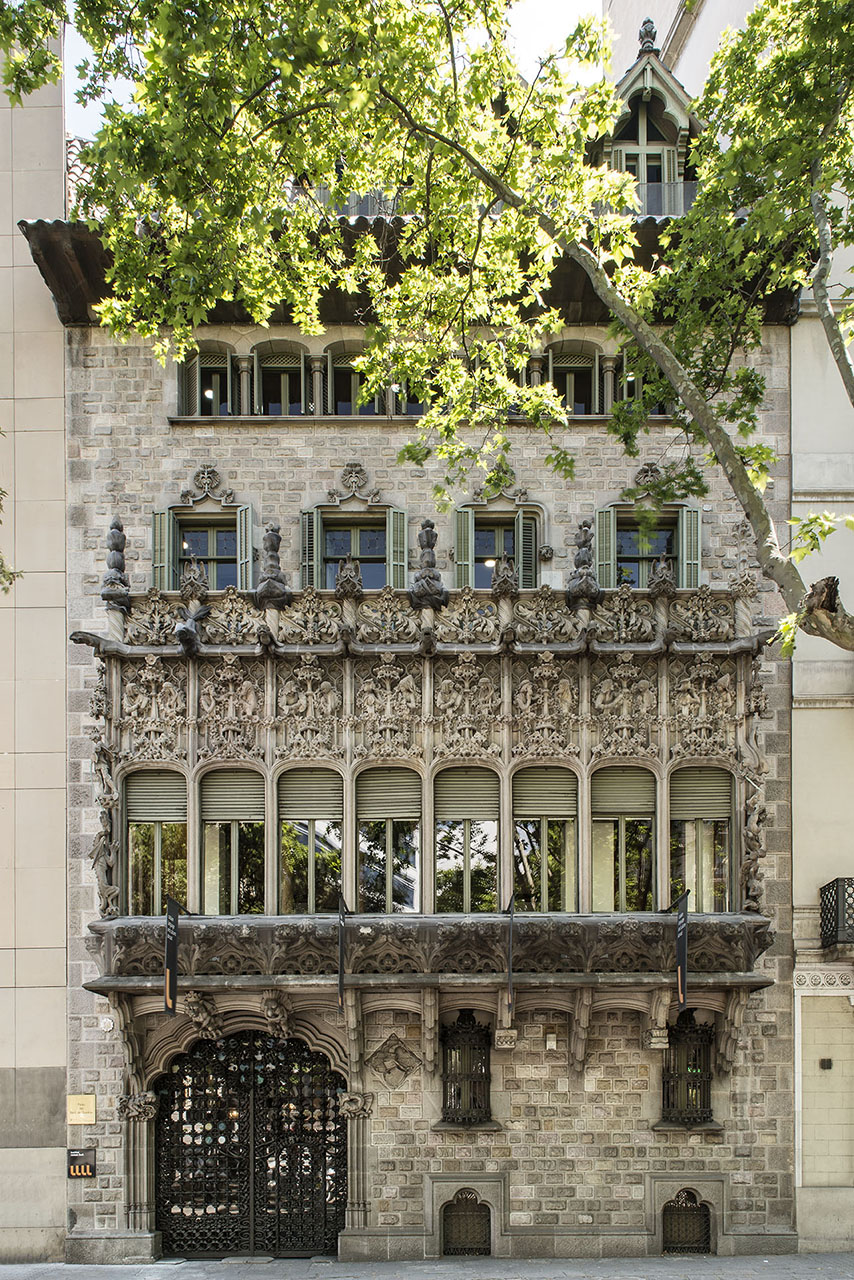
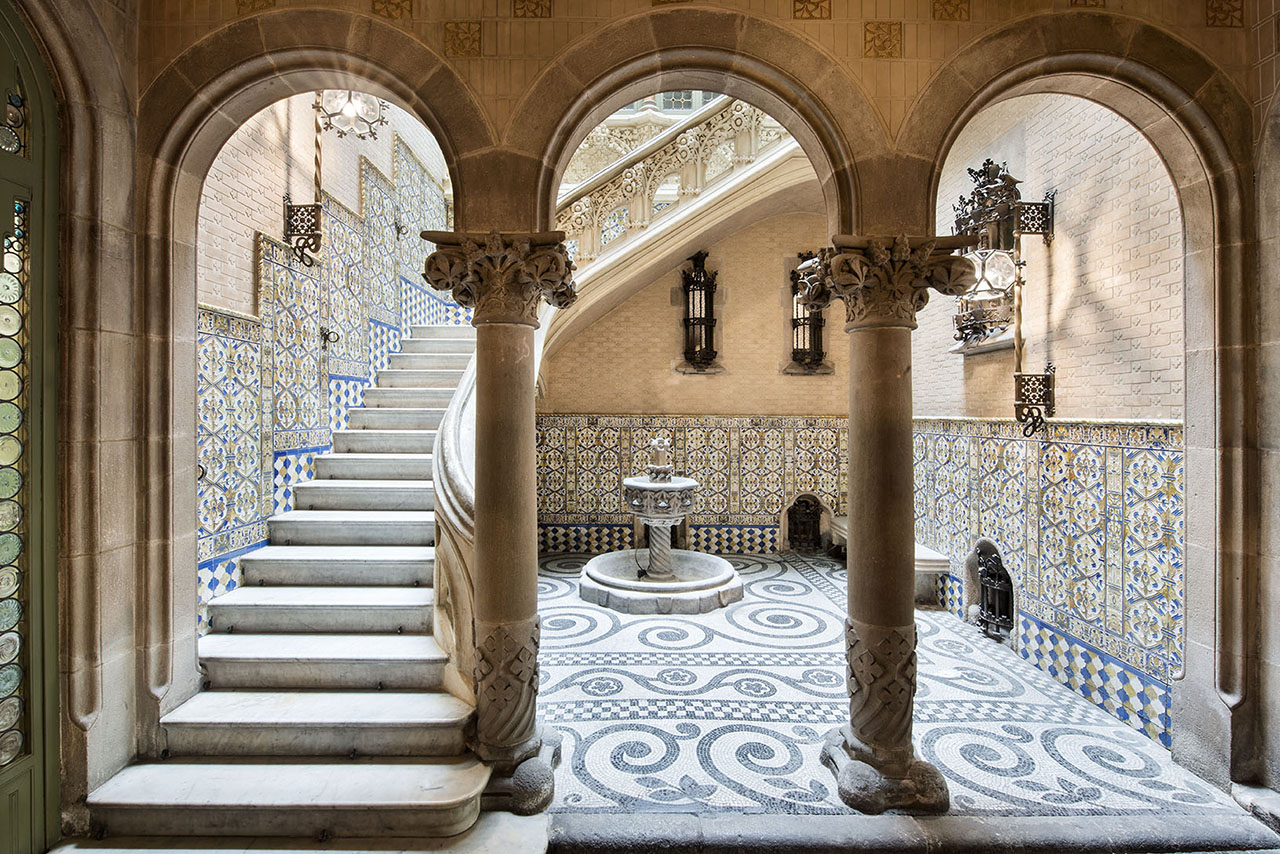
El Palau del Baró de Quadras
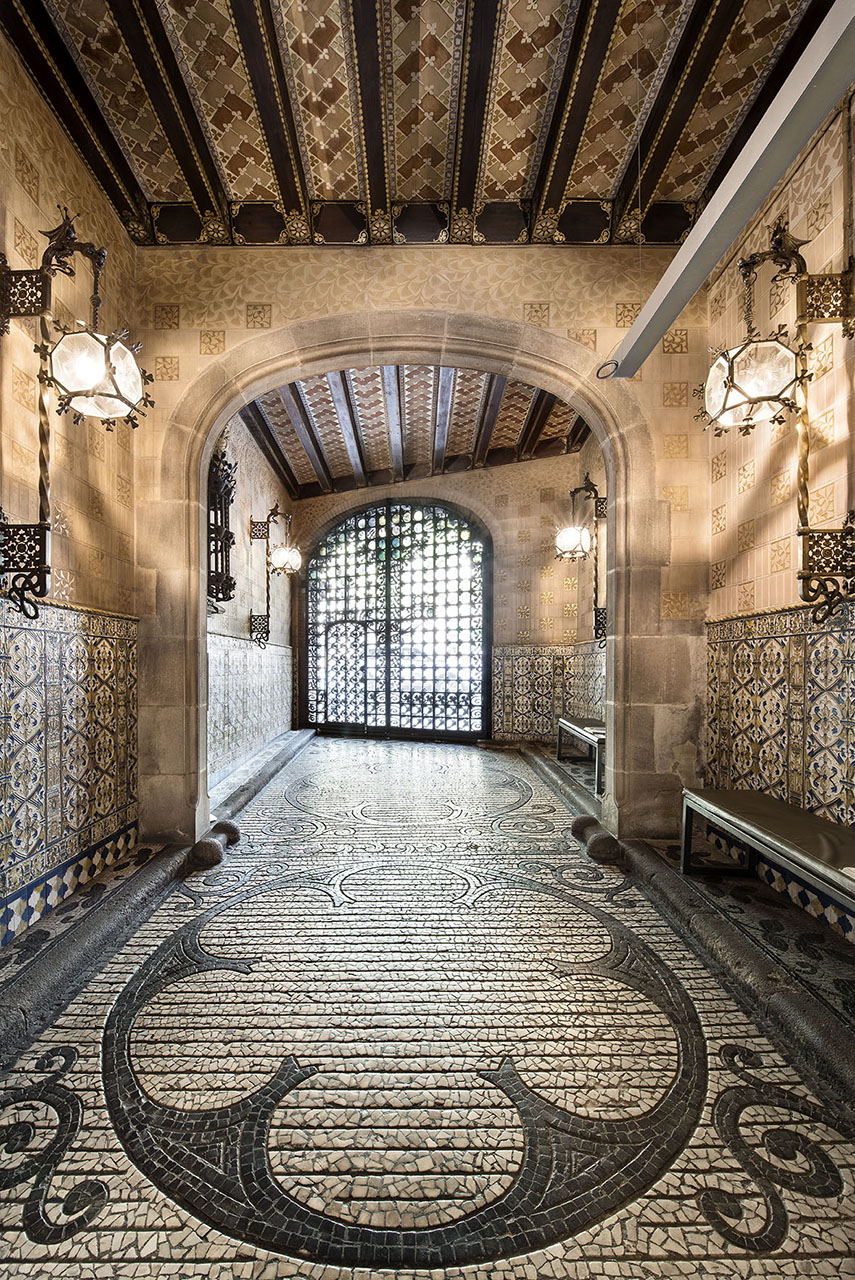
Starting with a thorough renovation of an existing building on a narrow plot of land that faced Carrer Rosselló—and did not yet open on to Avinguda Diagonal at the back—Puig i Cadafalch created this small Modernista jewel: not only the façade, but also the front and back doors leading to the grand central entrance hall with its staircase up to the first floor, contribute to making it one of the most successful projects of its time.
The palace is very much in keeping with typical buildings from that period in the Eixample neighborhood: the first floor reserved for the owners and the other floors for rent. The ground floor provided access to the upper floors and service quarters, and served as the formal entrance to the Baron's residence. A carriage entryway—unusual in its access from both streets—opening on to the grand staircase leading to the first floor, is a focal point of this residence and a nod to the Gothic palaces in Barcelona, most of which are located on Carrer Montcada.
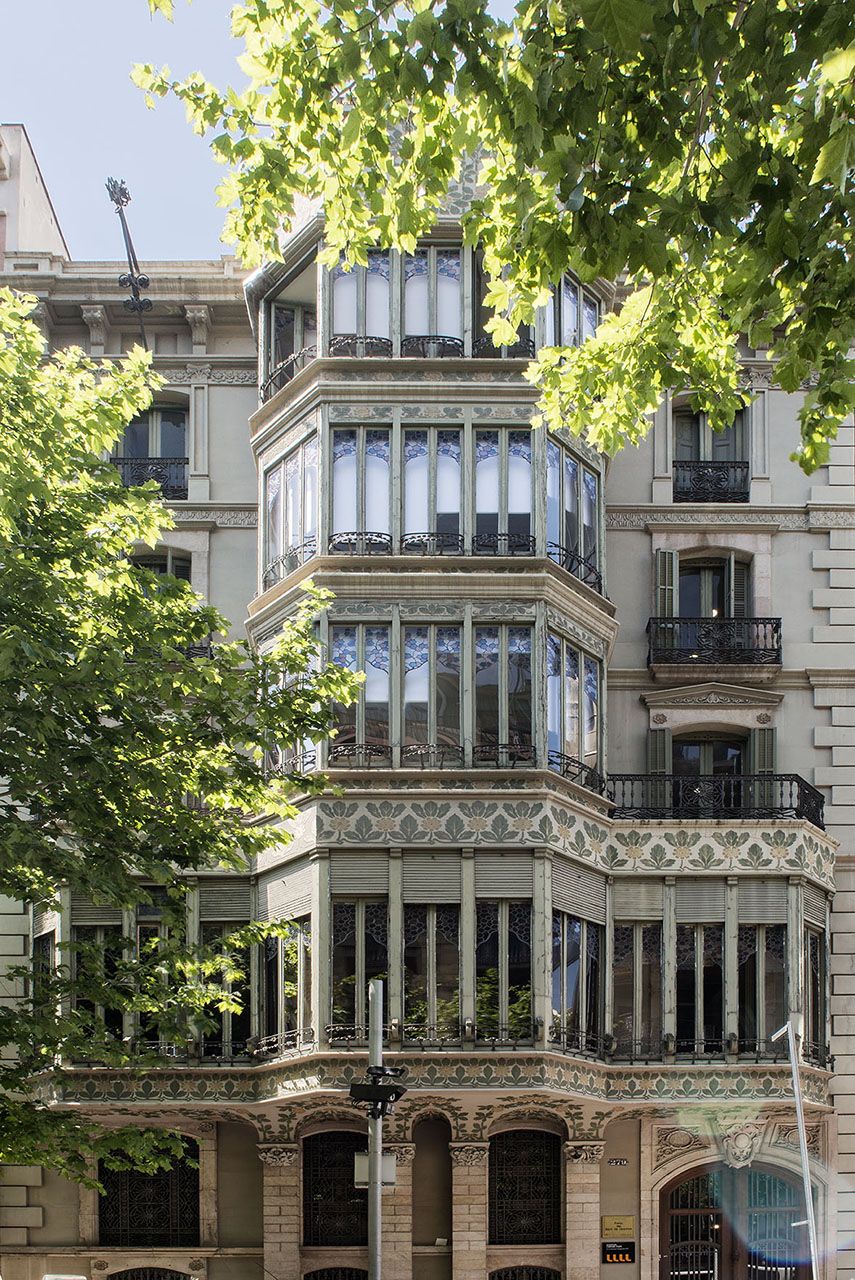
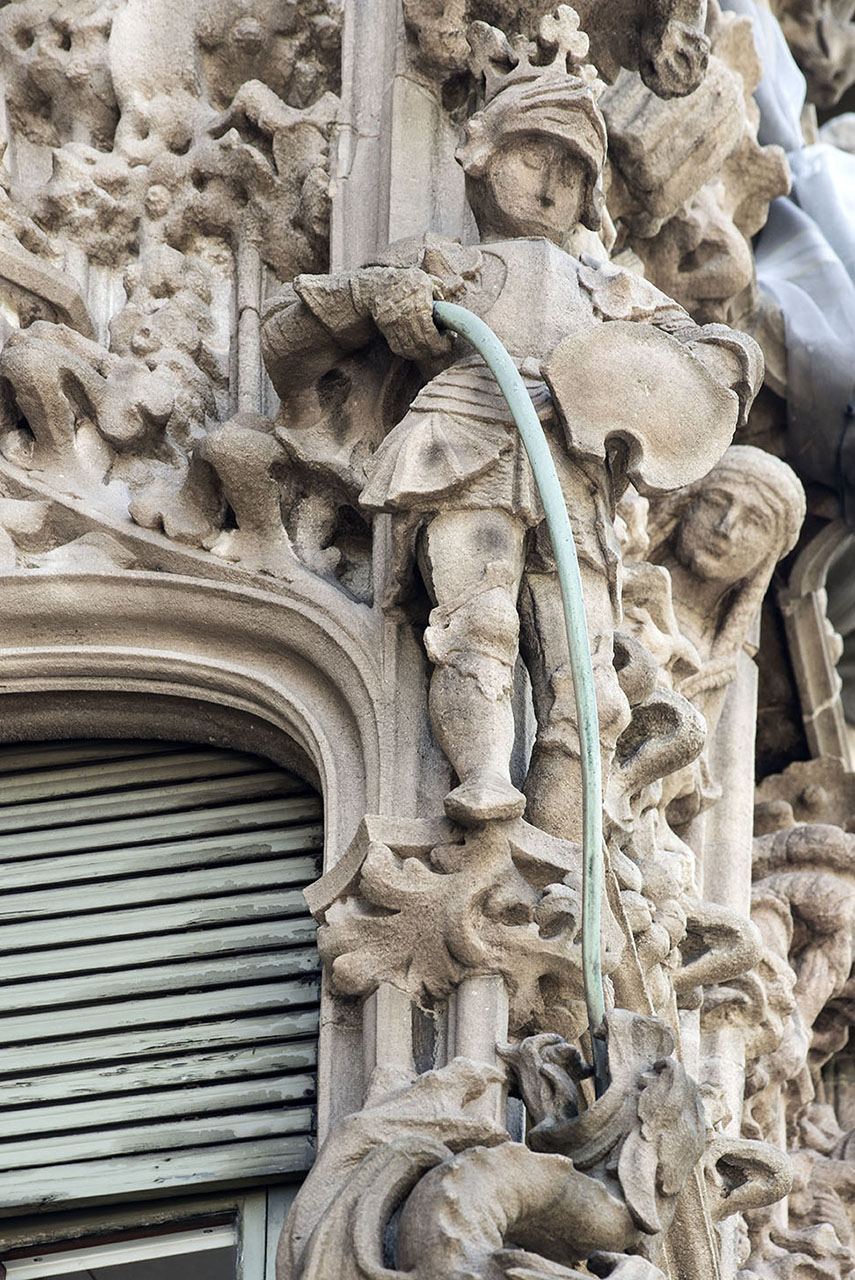
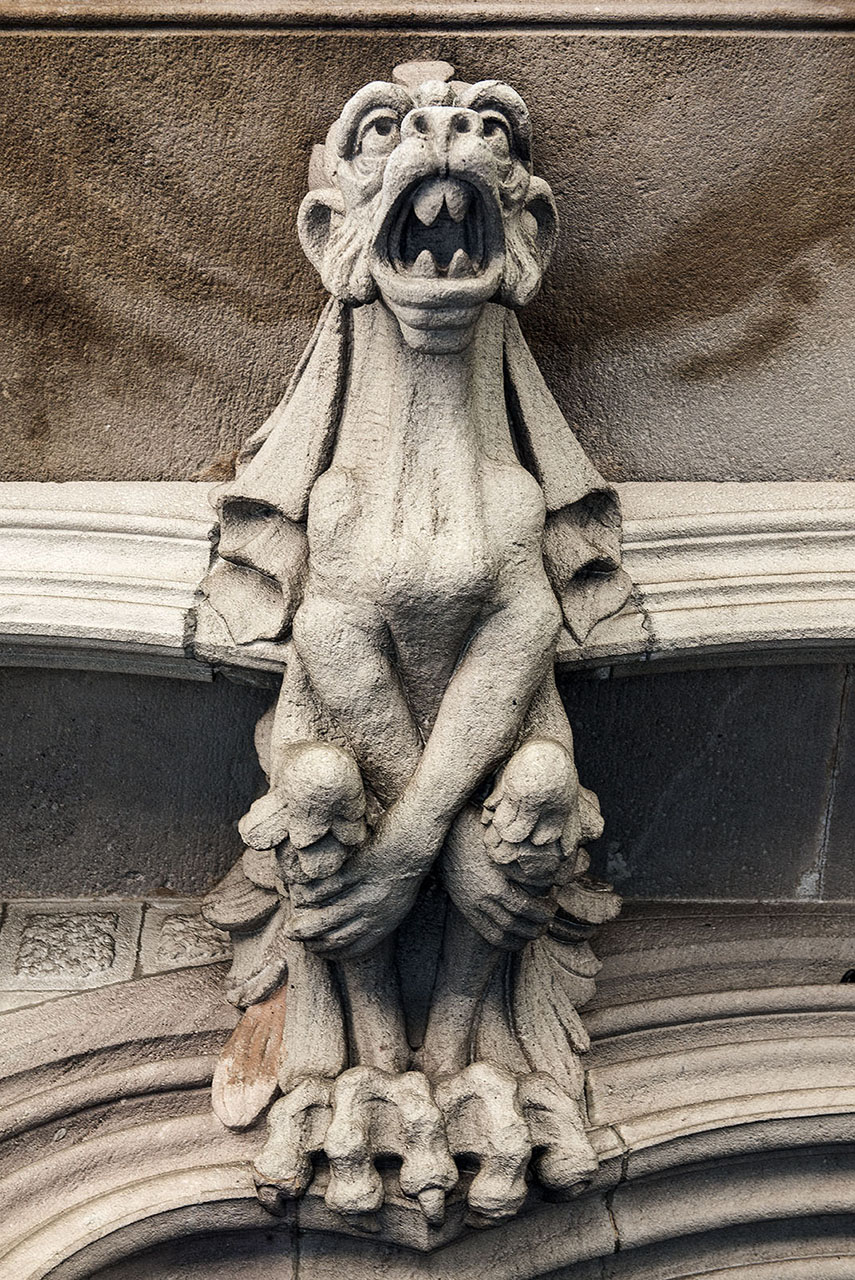
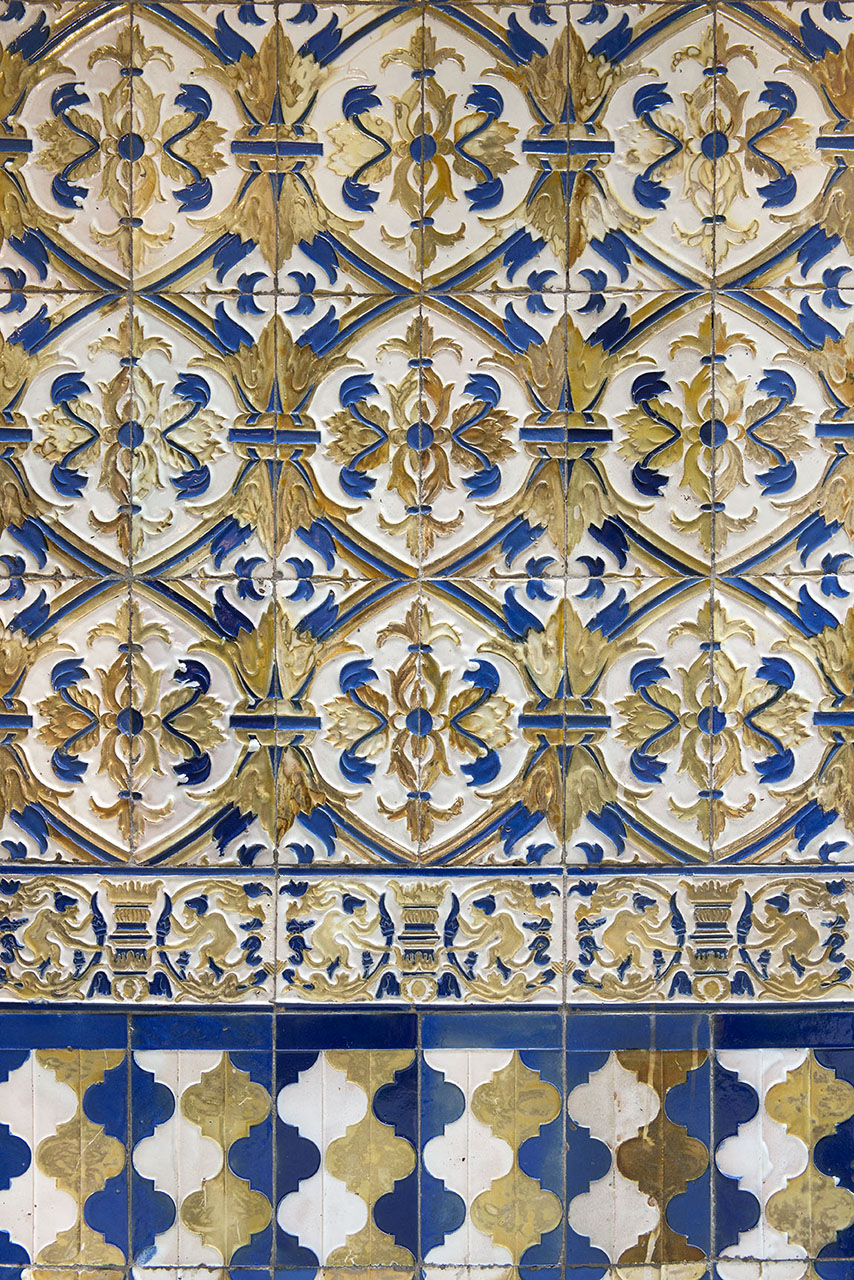
The way the Eixample was designed, the buildings tend to have two markedly different facades: one formal and elaborate, facing the street, and the other, facing the back and an inner courtyard, generally simpler and unassuming. This dichotomy is evident in the Palau del Baró de Quadras, as well: the Avinguda Diagonal façade, where artisans Alfons Juyol and Eusebi Arnau used carved stone for their design of one of the most impressive Gothic revival balconies seen in Modernista architecture; and the rear façade, facing Carrer Rosselló, with its floral motifs extending horizontally and vertically along the three balconies and down the four floors.
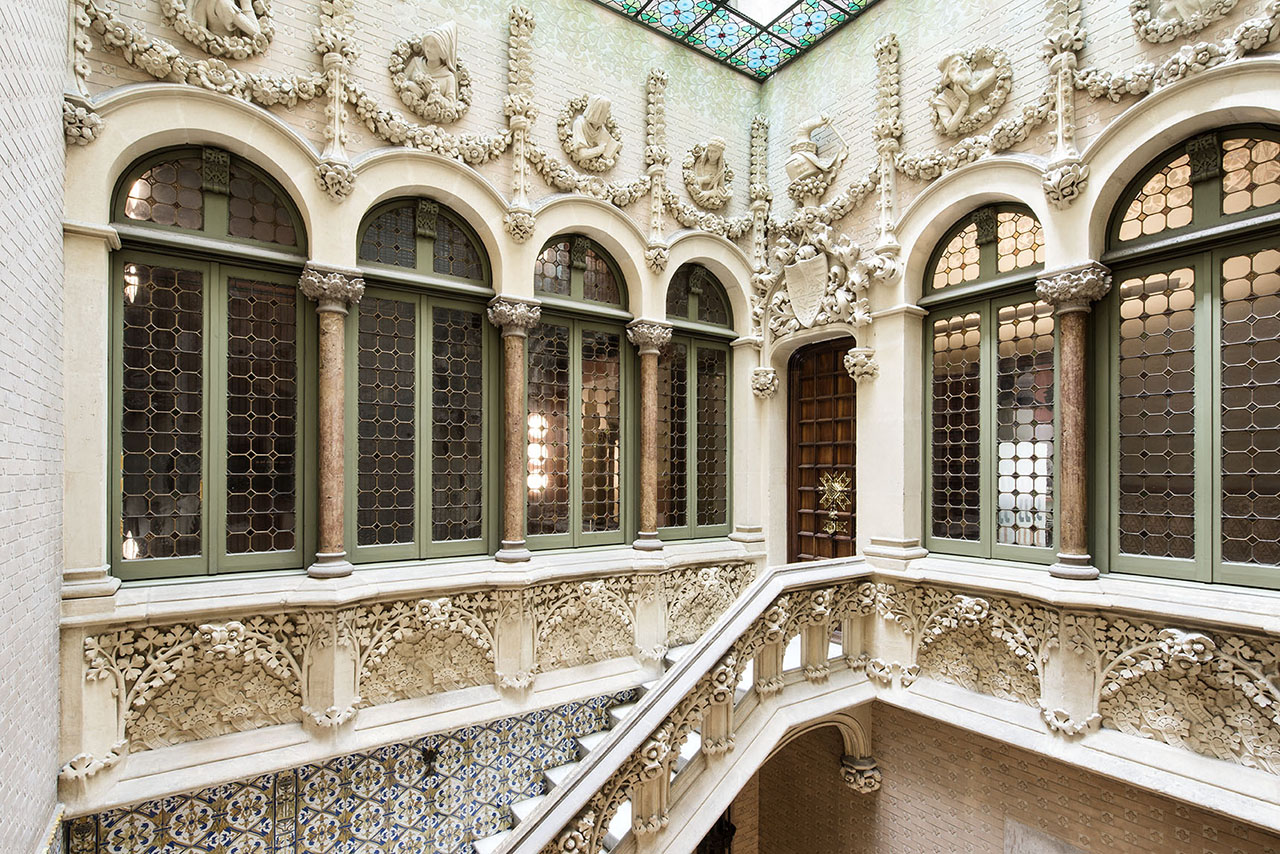

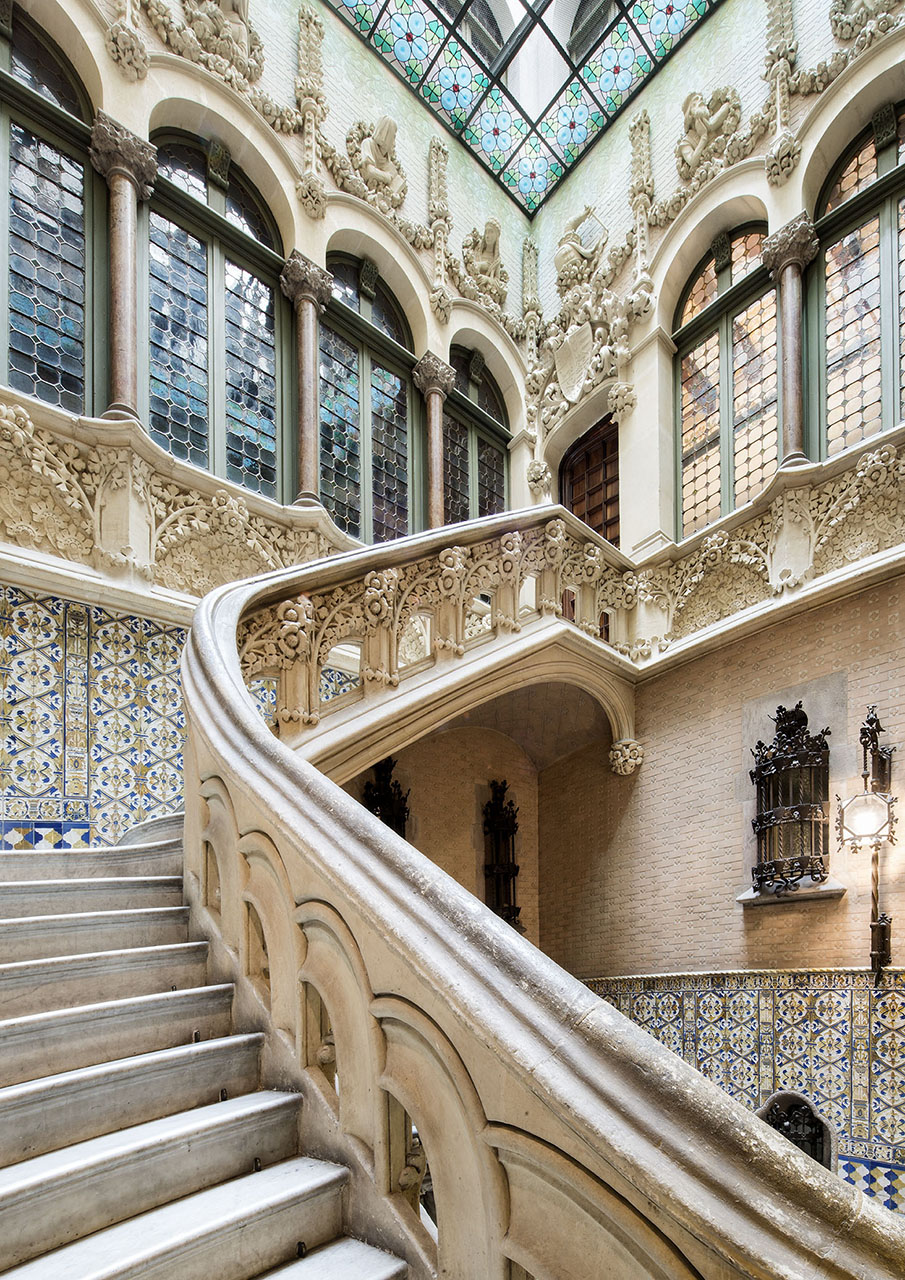
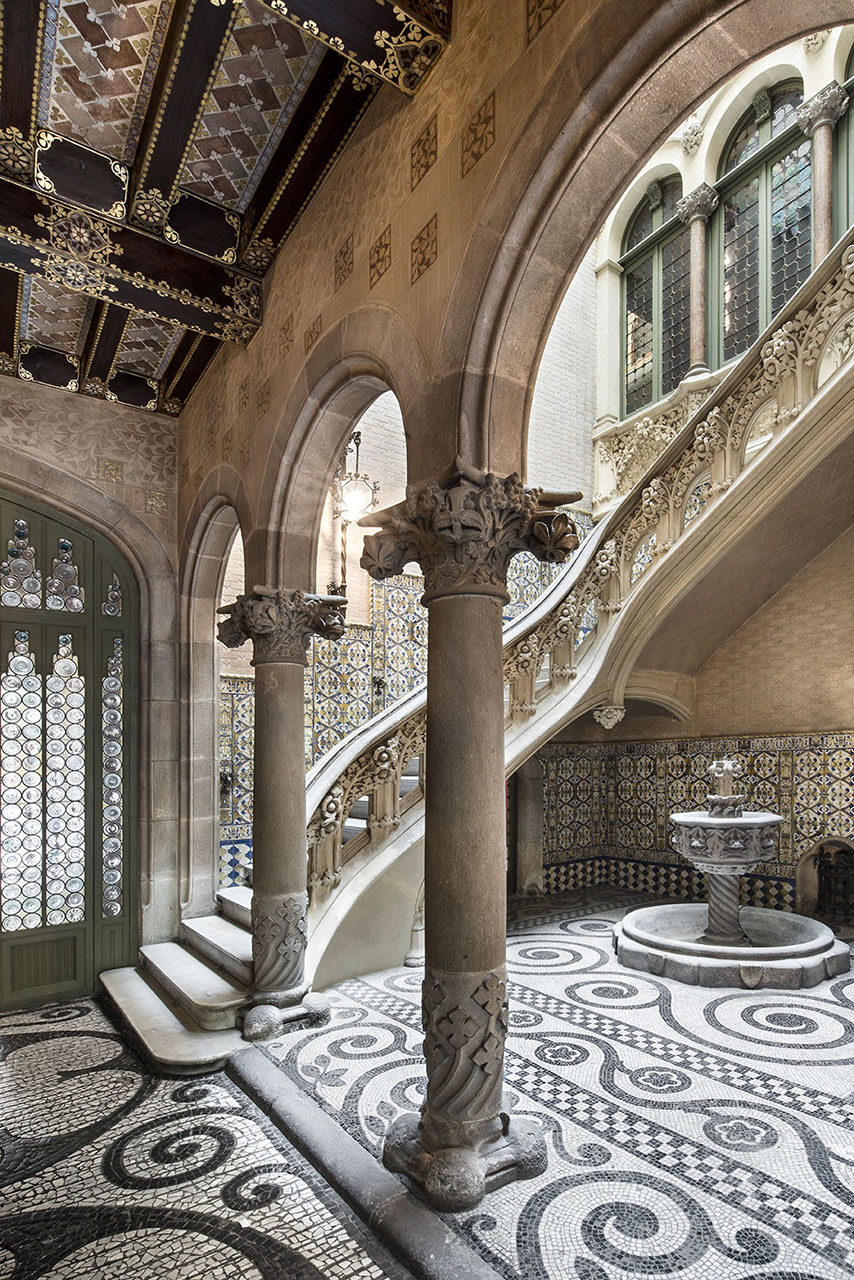
The Entryway and Staircase
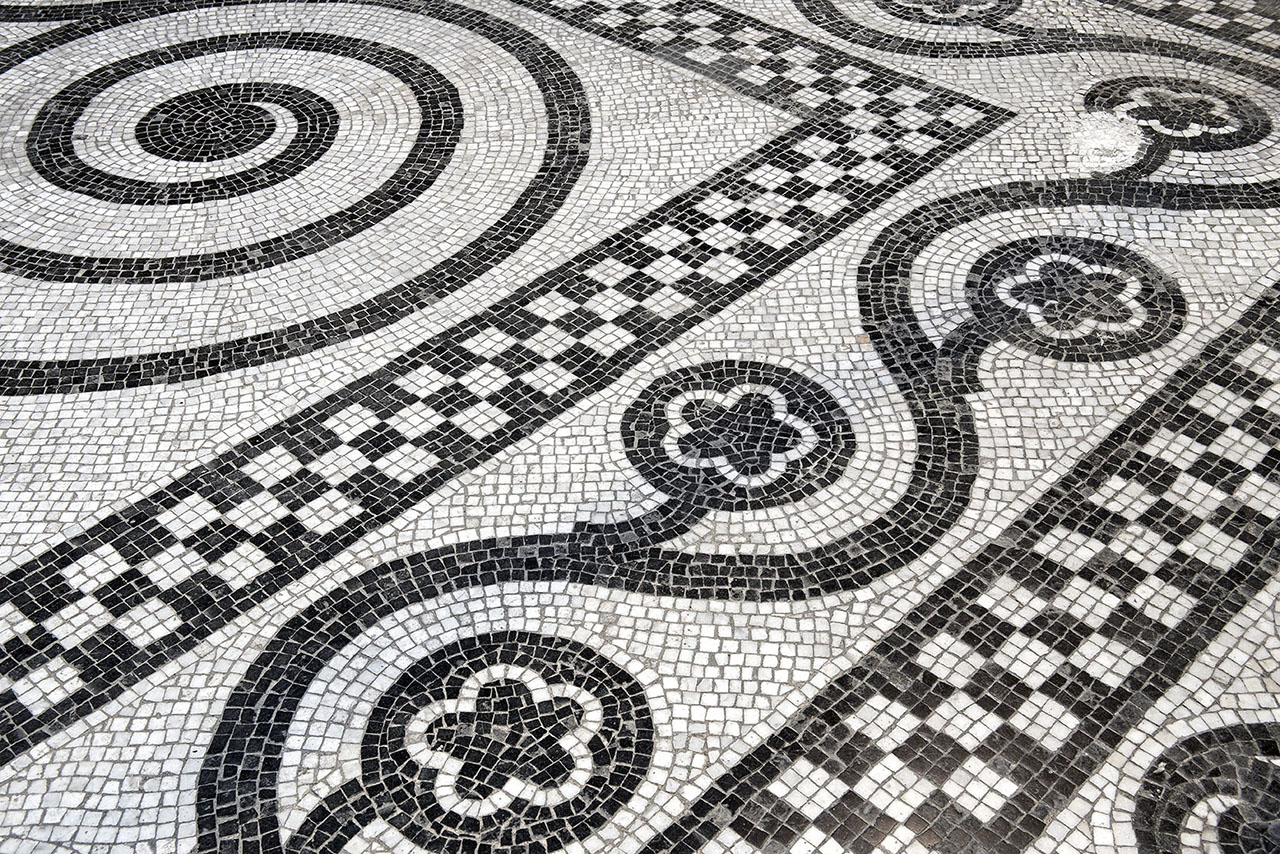
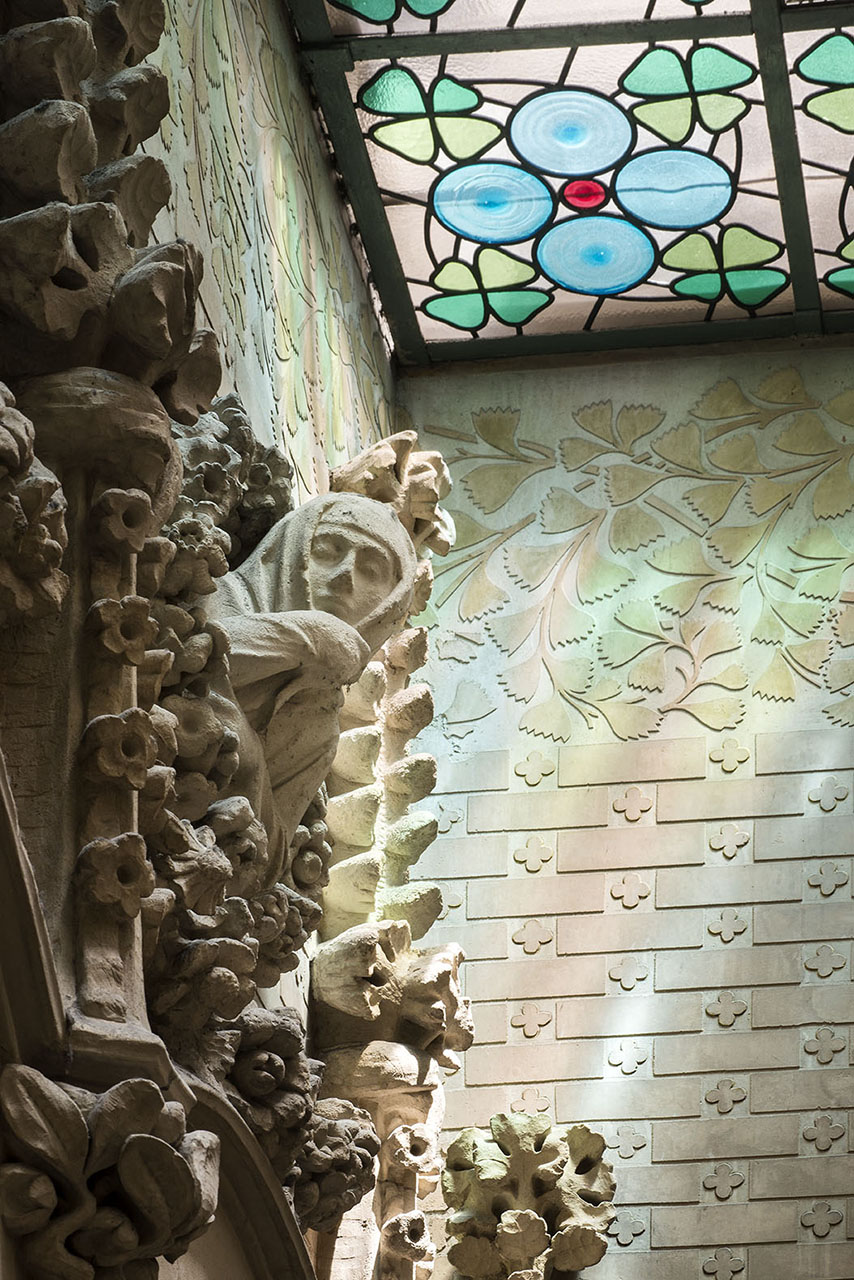
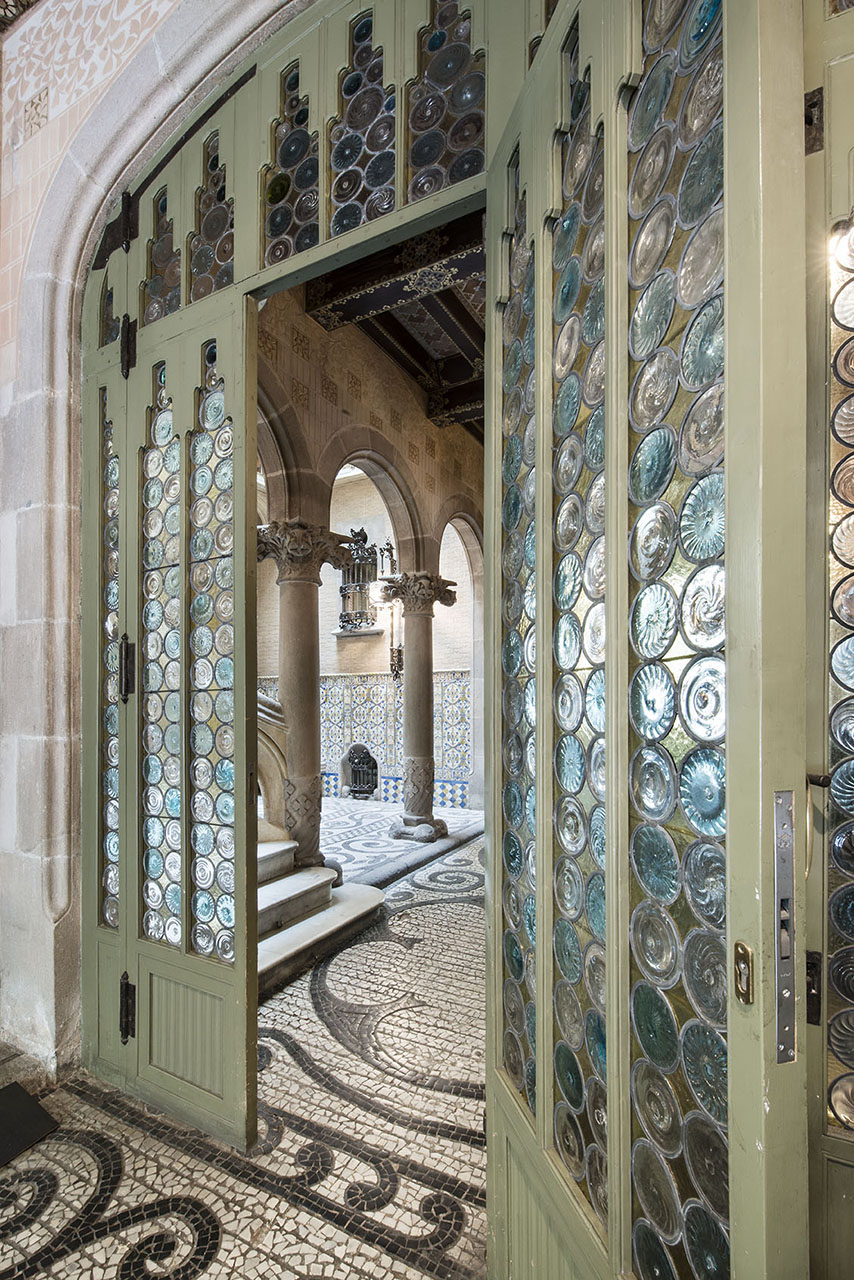
The importance the barons placed on the entryway is evident, not only in the elaborate decoration of the stairway and the glasswork on the skylight but also in the Roman mosaic flooring. Its central position provides the axis around which the stairwell and layout of the first floor revolve. The impressive iron grillwork on the ground floor doors, facing both Avinguda Diagonal and Carrer Rosselló, were forged by master ironworker Manuel Ballarín i Lancuentra.




The Salons
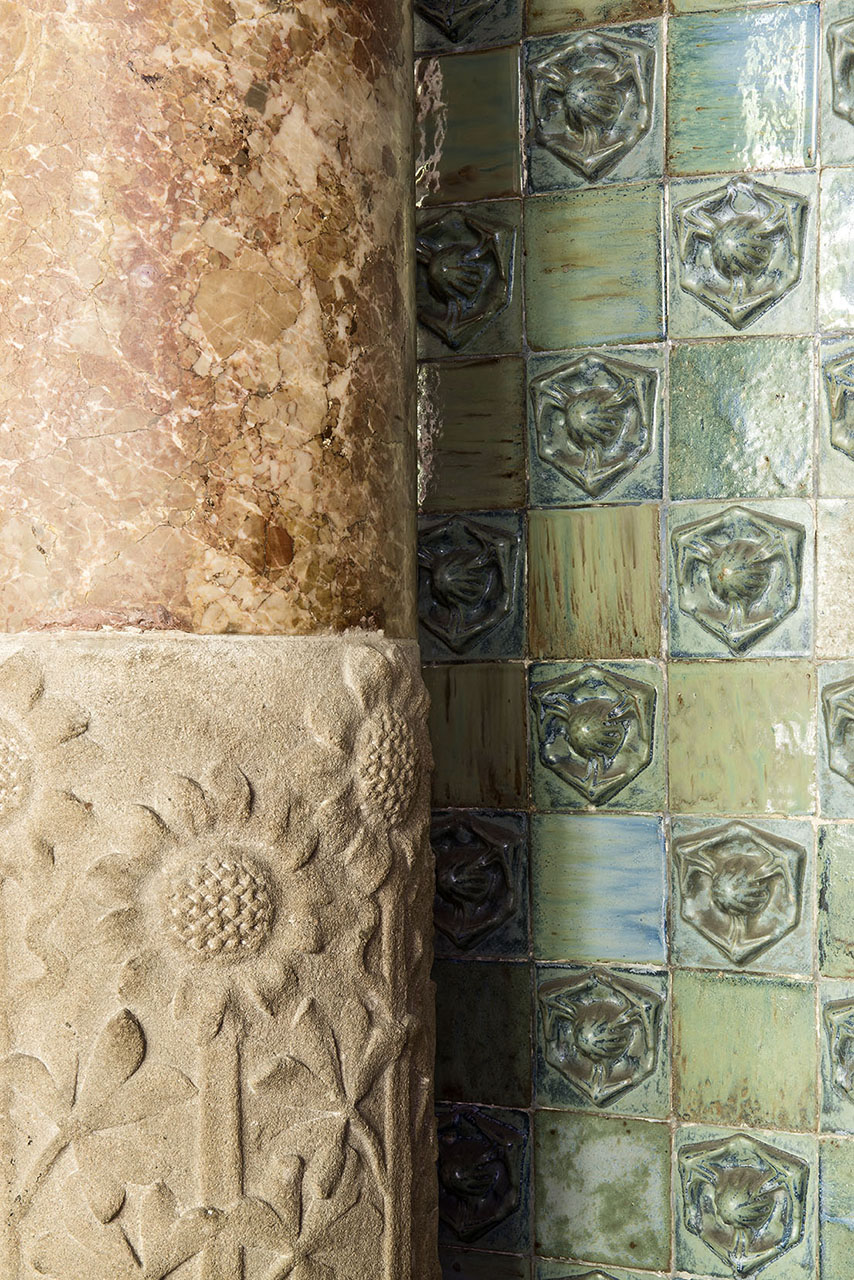
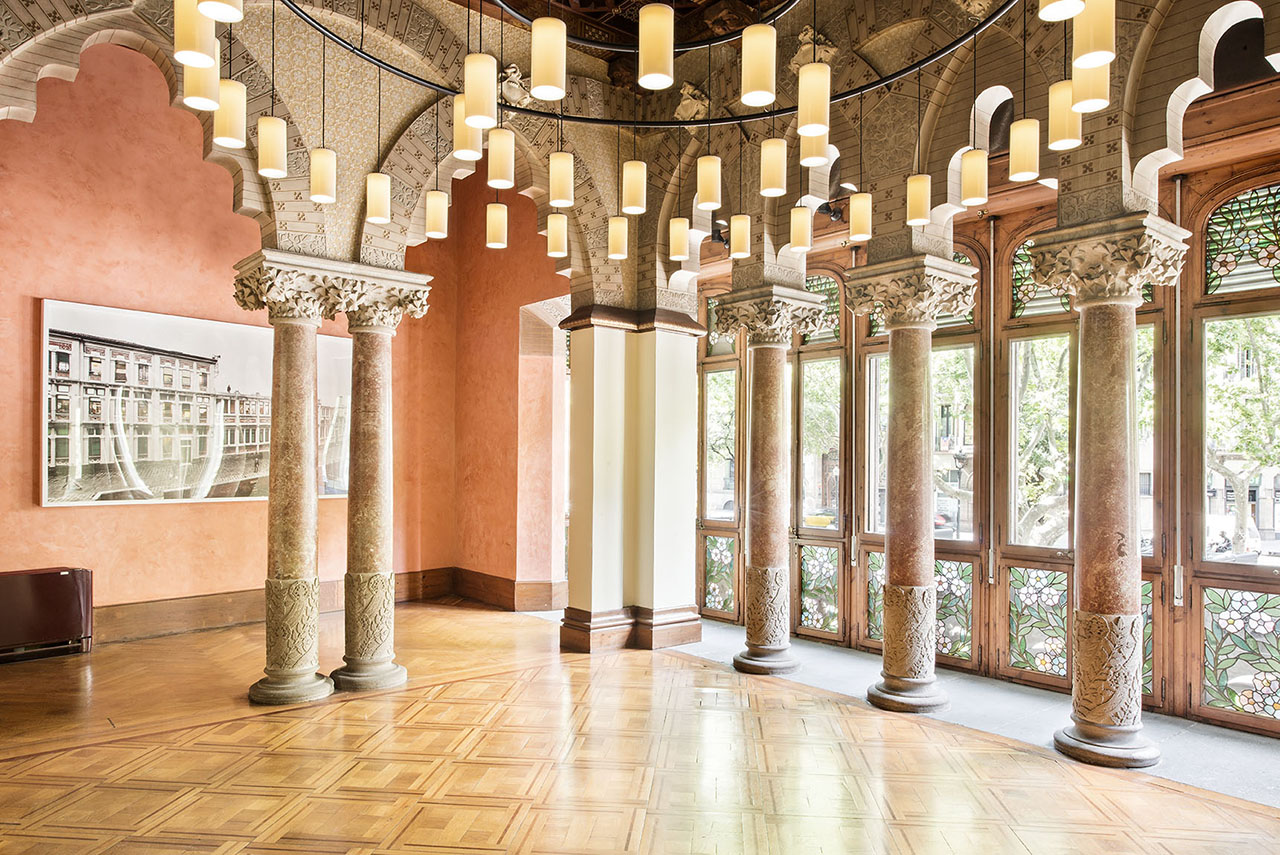
The large rooms facing Avinguda Diagonal are the most public spaces in the building and meant for receiving visitors. They feature Moorish-style stone arches with colorful ceramic floral motifs and Gothic sculptural elements.
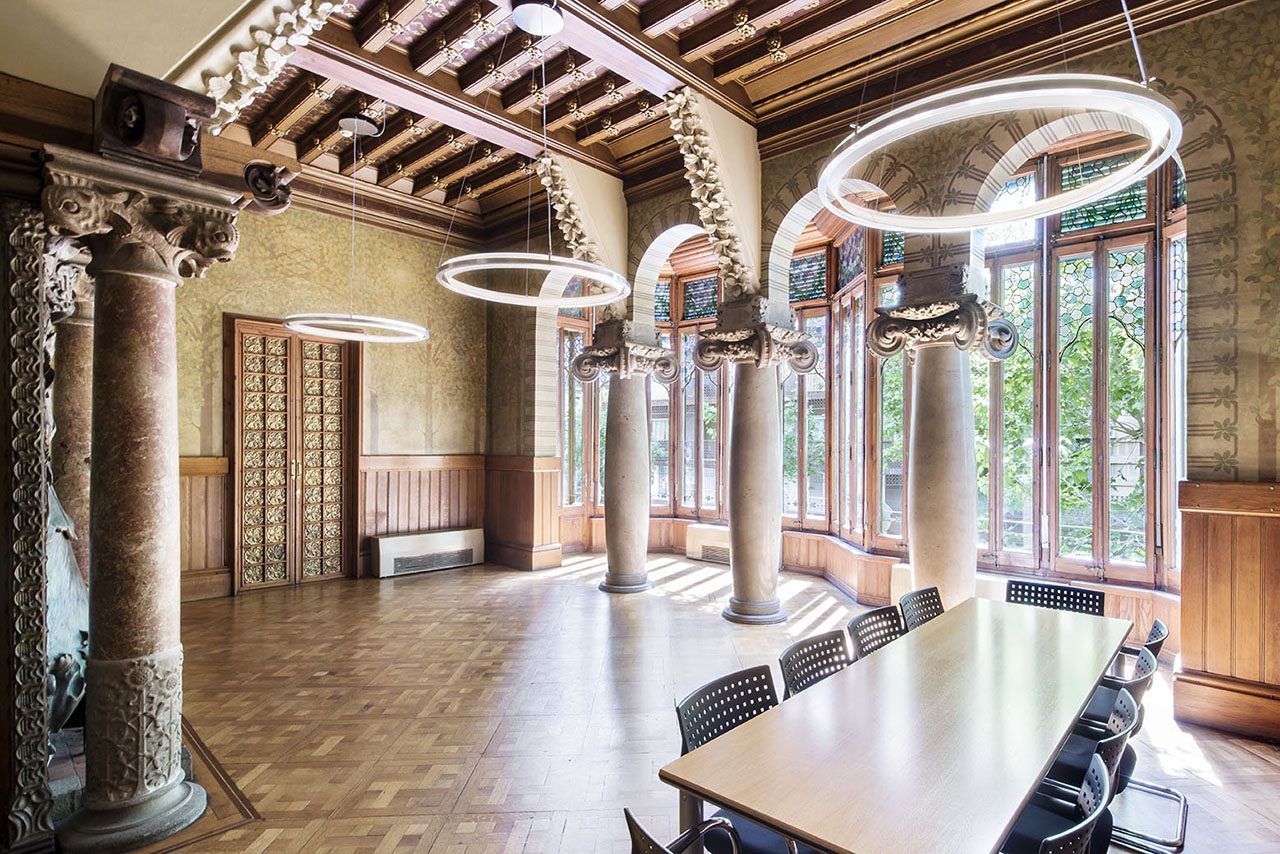
The spaces that face Carrer Rosselló were designed for family use, with more detailed floral stucco relief work gracing the walls. Bold Ionic columns covered with floral and plant motifs, in the English Arts and Crafts style, face the fireplace, the symbol of home life.
Also worthy of note is the extraordinary woodwork of the coffered ceilings and the hardwood flooring with various geometric designs.
EThe Palau was designated a National Historical Monument of Cultural Interest on January 9, 1976.


Restoration of architectural features
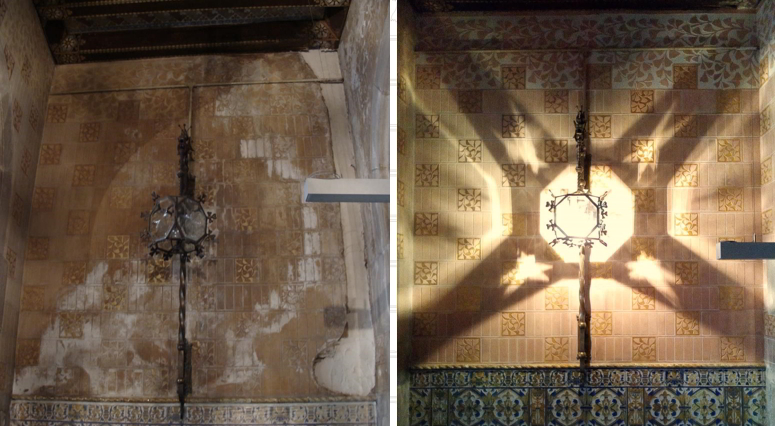
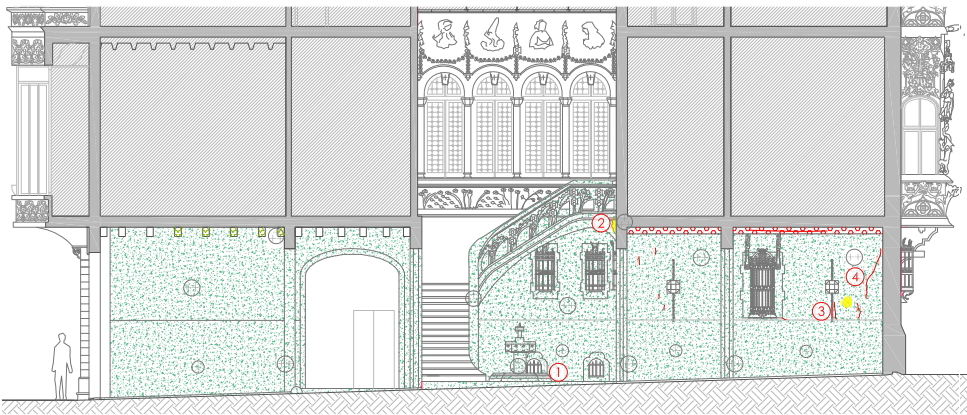
During the second half of 2015 a first phase of preventative restoration and conservation of the architectural and ornamental features of the entrance to the Palau Baró de Quadras was carried out. This restoration has allowed the important patrimonial relevance of this part of the building, which is a benchmark of Modernism in Barcelona, to be truly appreciated.
Architect Àngel Gil and restorers of cultural assets Anna González and Josep Pasqual were given the job of carrying out the study for the renovation of the vestibule of the Palau and the first stage of the work.
The restorers made a visual study with the aim of getting to know the constructive definition and the state of preservation of the different materials and decorative features. In this way, they were able to diagnose the problems in the building’s vestibule and establish priorities for action.
The study concluded that the vestibule of the Palau was showing signs of varying degrees of degradation that distorted the viewer’s perception, whether due to changes in the colours or the volumes.
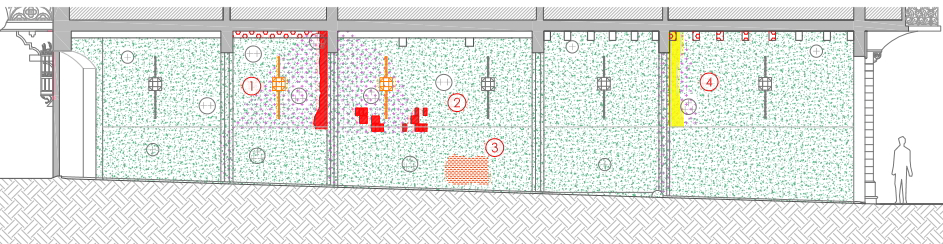
Actions to conserve the vestibule
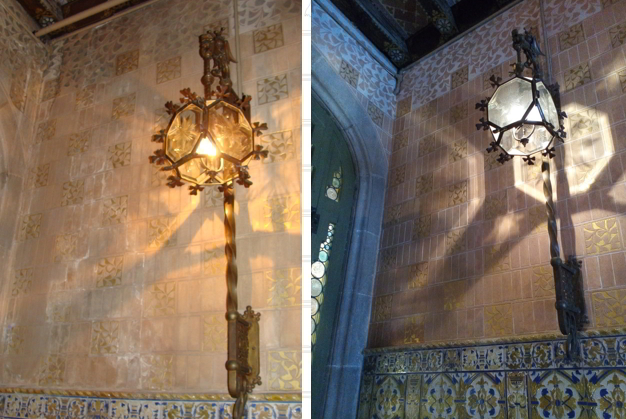
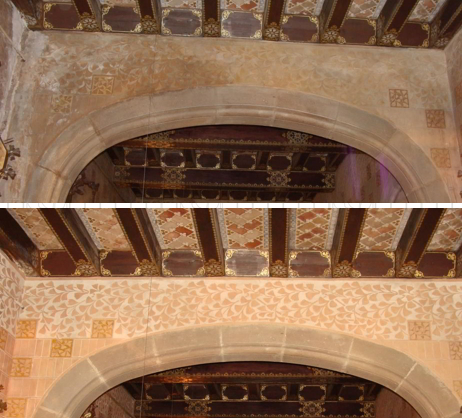
The restorers planned a series of conservation actions based on intervention on elements of stone, mosaics, tiles, sgraffiti and ceiling coffering, and another series of actions on the wrought iron railings, the wooden door in Carrer de Rosselló and the bronze lamps.
The project carried out has been subjected to professional criteria of maximum conservation of the original work, reversibility, the use of traditional techniques and maximum research.
The restoration work has made it possible to halt the damage and the causes of deterioration, while at the same time recovering the material physical integrity and the aesthetic beauty of this vestibule, designed and built by Puig i Cadafalch.
Palau Baró de Quadras / Avda Diagonal, 373 · BCN (08008) / Telf. +34 934678000 / espais@llull.cat